Applying Best Practices
On the long term, the survival of any company strongly depends on its ability to continuously adapt to ever changing market conditions.
Efyca supports your continuous improvement program by providing the best proven process improvement methodologies so that you can innovate faster and more successfully:
- Capability Maturity Model Integration
- Lean manufacturing
- Six-sigma
- Theory of Constraints
Capability Maturity Model Integration
Capability Maturity Model Integration is a collection of best practices organized in a wide variety of process areas:
-
- Organizational Performance Management
- Causal Analysis and Resolution
- Quantitative Project Management
- Organizational Process Performance
-
- Strategic Service Management
- Service System Development
- Service System Transition
- Service Delivery
- Incident Resolution and Prevention
- Service Continuity
-
- Requirements Development
- Technical Solution
- Product Integration
- Verification
- Validation
-
- Integrated Project Management
- Requirements Management
- Capacity and Availability Management
- Project Planning
- Risk Management
- Supplier Agreement Management
- Project Monitoring and Control
-
- Organizational Process Definition
- Organizational Process Focus
- Organizational Training
-
- Decision Analysis and Resolution
- Measurement and Analysis
- Process and Product Quality Assurance
- Configuration Management

Lean Manufacturing
Derived from the Toyota Production System, Lean is focused on the reduction of all types of activities that introduce “muda” (waste), “mura” (variation) and “muri” (overload) and preserve only the activities that add value.

Activities that are actually performed but do not add any value to the customer should be minimized if not completely removed, for instance:
- Storing raw materials, work in progress or finished goods
- Moving people and products around the working area
- Waiting time due to dependencies or interruptions in the process
- Poor tool or product design leading to over processing
- Inspecting products and fixing defects
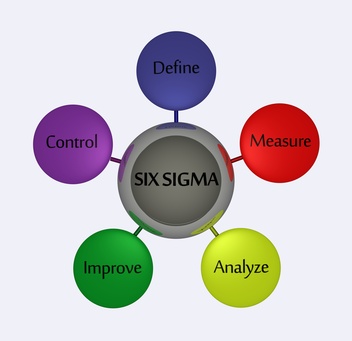
Six Sigma
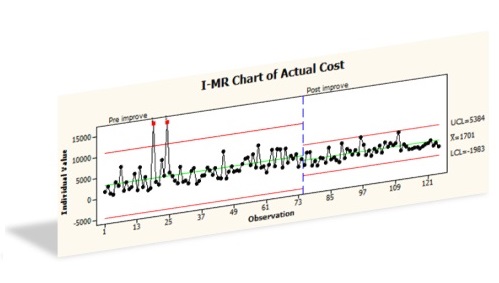
Six sigma seeks to improve the quality of the output by applying statistical techniques to identify and removing causes of defects.
Its main process is called DMAIC which is an acronym of its 5 steps:
- Define: set the process improvement goal
- Measure: identify and measure potential performance factors
- Analyze: apply statistical techniques to the collected data to identify key factors which has a demonstrated cause-and-effect relationship with the output
- Improve: optimize the process to address the key factors
- Control: implement control systems to continuously monitor the process
Theory of Constraints (TOC)
TOC approaches process improvement from the systems point of view. Any organization is a system which performance can be measured by its throughput.
At any given time the performance depends on a single constraint, so to improve the system performance you should:

- Identify the system’s constraint
- Decide how to exploit the constraint
- Subordinate everything else to the decision
- Elevate the system’s constraint
- Once the constraint has been broken, go back to step 1